Strontium has 4 isotopes, 84Sr, 86Sr, 87Sr and 88Sr. One of ...
Read More How to Minimize Sample Preparation and Optimize Sr Isotope Ratio Analysis
Your educational resource for biopharma, pharma, environmental, food and agriculture, industrial, and clinical labs
Your educational resource for biopharma, pharma, environmental, food and agriculture, industrial, and clinical labs

Strontium has 4 isotopes, 84Sr, 86Sr, 87Sr and 88Sr. One of ...
Read More How to Minimize Sample Preparation and Optimize Sr Isotope Ratio Analysis
I used to joke in graduate school that how fast I could actu...
Read More Tired of HPLC Downtime? Time for a Technology Boost?
Chlorinated dioxins and furans Dioxins are a collective term...
Read More What are Dioxins and PCBs, and What Type of GC-MS Should You Use to Analyze Them?
This is part two of a three-part series on Thermo Fisher Sci...
Read More Advanced LC-MS Tools and Software Solutions to Ease Your Metabolite Identification Challenges
This is the fifth in a five-part BioPharma Blog Series. Have...
Read More Unveiling Hidden Impurities: LC-HRMS for Biopharmaceutical Analysis
Water is a precious resource that is vital for all aspects o...
Read More Practical Analysis Solutions to Enhance Water Quality for a Safer Future
It’s World Water Day, but do we truly understand the impor...
Read More World Water Day: A Good Time to Reflect on the Critical Role of Water
In an era defined by environmental consciousness and operati...
Read More Water Management for Industrial and Chemical Manufacturers to Enhance Sustainability and Efficiency
Take a moment to reflect on the most impactful women in your...
Read More Celebrating Women’s History Month: A Tribute to Our Sheroes!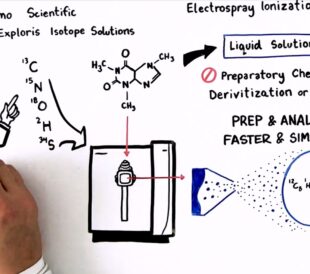
Achieving breakthrough scientific discoveries is hard, requi...
Read More How to Optimize Your Natural Abundance Isotope Ratio Analysis – Watch the Video